
Ethical Hacking Basic Concepts
Ethical Hacking identifies the vulnerabilities or weaknesses in a computer system or a network and devises a strategy for protecting those vulnerabilities. In this article, we will cover all the basic concepts related to Ethical Hacking.
Hacking is a process of identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities in computer and network systems to gain access to these systems. Password cracking is a type of hacking used to gain access to the system. Hacking is a fraudulent act that allows criminals to invade a system, steal personal data, or perform fraud in any manner via digital devices.
Hacking definition: What is hacking?
Hacking refers to activities that seek to compromise digital devices, such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and even entire networks. And while hacking might not always be for malicious purposes, nowadays most references to hacking, and hackers, characterize it/them as unlawful activity by cybercriminals—motivated by financial gain, protest, information gathering (spying), and even just for the “fun” of the challenge.
Hacking refers to the misuse of devices like computers, smartphones, tablets, and networks to cause damage to or corrupt systems, gather information on users, steal data and documents, or disrupt data-related activity.
A traditional view of hackers is a lone rogue programmer who is highly skilled in coding and modifying computer software and hardware systems. But this narrow view does not cover the true technical nature of hacking. Hackers are increasingly growing in sophistication, using stealthy attack methods designed to go completely unnoticed by cybersecurity software and IT teams. They are also highly skilled in creating attack vectors that trick users into opening malicious attachments or links and freely giving up their sensitive personal data.
Black Hat Hackers
Black hat hackers are the “bad guys” of the hacking scene. They go out of their way to discover vulnerabilities in computer systems and software to exploit them for financial gain or for more malicious purposes, such as to gain reputation, carry out corporate espionage, or as part of a nation-state hacking campaign.
These individuals’ actions can inflict serious damage on both computer users and the organizations they work for. They can steal sensitive personal information, compromise computer and financial systems, and alter or take down the functionality of websites and critical networks.
White Hat Hackers
White hat hackers can be seen as the “good guys” who attempt to prevent the success of black hat hackers through proactive hacking. They use their technical skills to break into systems to assess and test the level of network security, also known as ethical hacking. This helps expose vulnerabilities in systems before black hat hackers can detect and exploit them.
The techniques white hat hackers use are similar to or even identical to those of black hat hackers, but these individuals are hired by organizations to test and discover potential holes in their security defenses.
Grey Hat Hackers
Grey hat hackers sit somewhere between the good and the bad guys. Unlike black hat hackers, they attempt to violate standards and principles but without intending to do harm or gain financially. Their actions are typically carried out for the common good. For example, they may exploit a vulnerability to raise awareness that it exists, but unlike white hat hackers, they do so publicly. This alerts malicious actors to the existence of the vulnerability.
Script Kiddies
It is a known fact that half knowledge is always dangerous. The Script Kiddies are amateurs types of hackers in the field of hacking. They try to hack the system with scripts from other fellow hackers. They try to hack the systems, networks, or websites. The intention behind the hacking is just to get attention from their peers. Script Kiddies are juveniles who do not have complete knowledge of the hacking process.
Motives & Aims: One standard Kiddie Script attack is a DoS (Denial of Service) or DDoS attack (Distributed Denial of Service). This simply means that an IP address is flooded with too many excessive traffic that it collapses. Consider several Black Friday shopping websites, for instance. It creates confusion and prevents someone else uses the service.
Green Hat Hackers
Green hat hackers are types of hackers who’re learning the ropes of hacking. They are slightly different from the Script Kiddies due to their intention. The intent is to strive and learn to become full-fledged hackers. They are looking for opportunities to learn from experienced hackers.
Blue Hat Hackers
Blue Hat Hackers are types of hackers who’re similar to Script Kiddies. The intent to learn is missing. They use hacking as a weapon to gain popularity among their fellow beings. They use hacking to settle scores with their adversaries. Blue Hat Hackers are dangerous due to the intent behind the hacking rather than their knowledge.
Red Hat Hackers
Red Hat Hackers are synonymous with Eagle-Eyed Hackers. They are the types of hackers who’re similar to white hackers. The red hat hackers intend to stop the attack of black hat hackers. The difference between red hat hackers and white hat hackers is in the process of hacking through intention remains the same. Red hat hackers are quite ruthless while dealing with black hat hackers or counteracting with malware. The red hat hackers continue to attack and may end up having to replace the entire system set up.
Above are 7 types of hackers broadly referred to in the cybersecurity world.
The three types of hackers listed below work in different capacities.
State/Nation Sponsored Hackers
Government appoints hackers to gain information about other countries. These types of hackers are known as State/Nation sponsored hackers. They use their knowledge to gain confidential information from other countries to be well prepared for any upcoming danger to their country. The sensitive information aids to be on top of every situation but also to avoid upcoming danger. They report only to their governments.
Hacktivist
These types of hackers intend to hack government websites. They pose themselves as activists, so known as a hacktivist. Hacktivist can be an individual or a bunch of nameless hackers whose intent is to gain access to government websites and networks. The data gained from government files accessed are used for personal political or social gain.
Malicious insider or Whistleblower
These types of hackers include individuals working in an organization who can expose confidential information. The intent behind the exposure might be a personal grudge with the organization or the individual might have come across the illegal activities within the organization. The reason for expose defines the intent behind the exposure. These individuals are known as whistleblowers…
Hacking tools: How do hackers hack?
Hacking is typically technical in nature (like creating malvertising that deposits malware in a drive-by attack requiring no user interaction). But hackers can also use psychology to trick the user into clicking on a malicious attachment or providing personal data. These tactics are referred to as “social engineering.”
In fact, it’s accurate to characterize hacking as an over-arching umbrella term for activity behind most if not all of the malware and malicious cyberattacks on the computing public, businesses, and governments. Besides social engineering and malvertising, common hacking techniques include:
- Botnets
- Browser hijacks
- Denial of service (DDoS) attacks
- Ransomware
- Rootkits
- Trojans
- Viruses
- Worms
Phases of Hacking -:
The process of legal and authorized attempts to discover and successfully exploiting the computer system in an attempt to make the computer system more secure is called Ethical Hacking. This process includes a probe for vulnerability and providing proof of concept (POC) attacks to visualize that vulnerabilities are actually present in the system. A Good Penetration tester always provides a specific recommendation to remove the flaws in the system discovered during the penetration test. Penetration testing is also known by some other terms like
There are mainly 5 phases in hacking. Not necessarily a hacker has to follow these 5 steps in a sequential manner. It’s a stepwise process and when followed yields a better result.
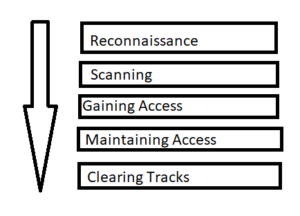
- Reconnaissance:
This is the first step of Hacking. It is also called as Footprinting and information gathering Phase. This is the preparatory phase where we collect as much information as possible about the target. We usually collect information about three groups,
Reconnaissance, also known as the preparatory phase, is where the hacker gathers information about a target before launching an attack and is completed in phases prior to exploiting system vulnerabilities. One of the first phases of Reconnaissance is dumpster diving. It is during this phase that the hacker finds valuable information such as old passwords, names of important employees (such as the head of the network department), and performs an active reconnaissance to know how the organization functions. As a next step, the hacker completes a process called footprinting to collect data on the security posture, reduces the focus area such as finding out specific IP addresses, identifies vulnerabilities within the target system, and finally draws a network map to know exactly how the network infrastructure works to break into it easily. Footprinting provides important information such as the domain name, TCP and UDP services, system names, and passwords. There are also other ways to do footprinting, including impersonating a website by mirroring it, using search engines to find information about the organization, and even using the information of current employees for impersonation.
- Scanning:
In this phase, the hacker identifies a quick way to gain access to the network and look for information. There are three methods of scanning: pre-attack, port scanning/sniffing, and information extraction. Each of these phases demonstrates a specific set of vulnerabilities that the hacker can utilize to exploit the system’s weaknesses. The pre-attack phase is where the hacker scans the network for specific information based on the information gathered during reconnaissance. The port scanner or sniffing phase is where scanning includes the use of dialers, port scanners, vulnerability scanners, and other data-gathering equipment. The information extraction phase is where the attackers collect information about ports, live machines and OS details to launch an attack.
Three types of scanning are involved:
- Port scanning: This phase involves scanning the target for the information like open ports, Live systems, various services running on the host.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Checking the target for weaknesses or vulnerabilities which can be exploited. Usually done with help of automated tools
- Network Mapping: Finding the topology of network, routers, firewalls servers if any, and host information and drawing a network diagram with the available information. This map may serve as a valuable piece of information throughout the haking process.
- Gaining Access:
This phase is where an attacker breaks into the system/network using various tools or methods. After entering into a system, he has to increase his privilege to administrator level so he can install an application he needs or modify data or hide data.
- Maintaining Access:
The fourth phase of the ethical hacking process involves processes used to ensure the hacker can access the application for future use. A white-hat hacker continuously exploits the system for further vulnerabilities and escalates privileges to understand how much control attackers can gain once they get past security clearance. Some attackers may also try to hide their identity by removing any evidence of an attack and installing a backdoor for future access.
Hacker may just hack the system to show it was vulnerable or he can be so mischievous that he wants to maintain or persist the connection in the background without the knowledge of the user. This can be done using Trojans, Rootkits or other malicious files. The aim is to maintain the access to the target until he finishes the tasks he planned to accomplish in that target.
- Clearing Track:
Once the hacker gains access, they cover their tracks to escape the security personnel. They do this by clearing the cache and cookies, tampering the log files, and closing all the open ports. This step is important because it clears the system information making hacking a great deal harder to track.
No thief wants to get caught. An intelligent hacker always clears all evidence so that in the later point of time, no one will find any traces leading to him. This involves modifying/corrupting/deleting the values of Logs, modifying registry values and uninstalling all applications he used and deleting all folders he created.
To avoid any evidence that leads back to their malicious activity, hackers perform tasks that erase all traces of their actions. These include:
- Uninstalling scripts/applications used to carry out attacks
- Modifying registry values
- Clearing logs
- Deleting folders created during the attack
Ethical Hacking Concepts and Scope
What is Ethical Hacking?
- Ethical hacking involves the use of hacking tools, tricks, and techniques to identify vulnerabilitiesso as to ensure system security.
- It focuses on simulating techniques used by attackers to verify the existence of exploitable vulnerabilitiesin the system security.
- Ethical hackers performs security assessment of their organization with the permission of concerned authorities.
Why Ethical Hackingis Necessary
- To beat a hacker, you need to think like one!
- Ethical hacking is necessary as it allows to counter attacks from malicious hackersby anticipating methods used by them to break into a system.
- Reasons why Organizations Recruit Ethical Hackers:
- To prevent hackersfrom gaining access to organization’s information.
- To uncover vulnerabilitiesin systems and explore their potential as a risk.
- To analyze and strengthen an organization’s security postureincluding policies, network protection infrastructure, and end-user practices.
- Ethical Hackers Try to Answer the Following Questions:
- What can the intruder see on the target system? (Reconnaissance and Scanning phases)
- What can an intruder dowith that information? (Gaining Access and Maintaining Access phases)
- Does anyone at the target notice the intruders’ attemptsor successes? (Reconnaissance and Covering Tracks phases)
- If all the components of information systemare adequately protected, updated, and patched
- How much effort, time, and money is required to obtain adequate protection?
- Are the information security measuresin compliance to industry and legal standards?
Scope and Limitationsof Ethical Hacking
- Scope:
- Ethical hacking is a crucial component of risk assessment, auditing, counter fraud, and information systems security best practices.
- It is used to identify risksand highlight the remedial actions, and also reduces information and communications technology (ICT) costs by resolving those vulnerabilities.
- Limitations:
- However, unless the businesses first know what it is at that they are looking for and why they are hiring an outside vendor to hack systemsin the first place, chances are there would not be much to gain from the experience.
- An ethical hacker thus can only help the organization to better understand their security system, but it is up to the organization to place the right guards on the network.
Skills of an Ethical Hacker
- Technical Skills:
- Has in-depth knowledge of major operating environments, such as Windows, Unix, Linux, and Macintosh.
- Has in-depth knowledge of networkingconcepts, technologies and related hardware and software.
- Should be a computer expertadept at technical domains.
- Has knowledge of security areasand related issues.
- Has “high technical” knowledgeto launch the sophisticated attacks.
- Non-Technical Skills: Some of the non-technical characteristics of an ethical hacker include:
- Ability to learnand adapt new technologies quickly.
- Strong work ethics, and good problem solving and communication skills.
- Committed to organization’s security policies.
- Awareness of local standards and laws.
